Fissure in Ano
Are you experiencing sharp pain during bowel movements? Does the discomfort linger for hours afterward? You might be dealing with a fissure in ano – a small tear in the lining of the anal canal that can cause significant distress. 😖
While this condition may sound alarming, it's more common than you might think. Affecting people of all ages, fissures can turn a simple trip to the bathroom into a dreaded ordeal. But don't despair! Understanding this condition is the first step towards finding relief and preventing future occurrences.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the world of anal fissures, exploring everything from diagnosis to treatment options. We'll uncover the secrets of conservative management, discuss surgical interventions when necessary, and reveal lifestyle changes that can keep your bottom happy and healthy. 🍑💪 So, let's embark on this journey to better anal health and bid farewell to the pain that's been a real pain in the... well, you know where!
Understanding Fissure in Ano
Definition and Causes
A fissure in ano, also known as an anal fissure, is a small tear or cut in the lining of the anal canal. This condition typically occurs when passing hard or large stools, leading to trauma in the delicate anal tissue. Common causes include:
- Chronic constipation
- Passing large, hard stools
- Prolonged diarrhea
- Childbirth
- Anal intercourse
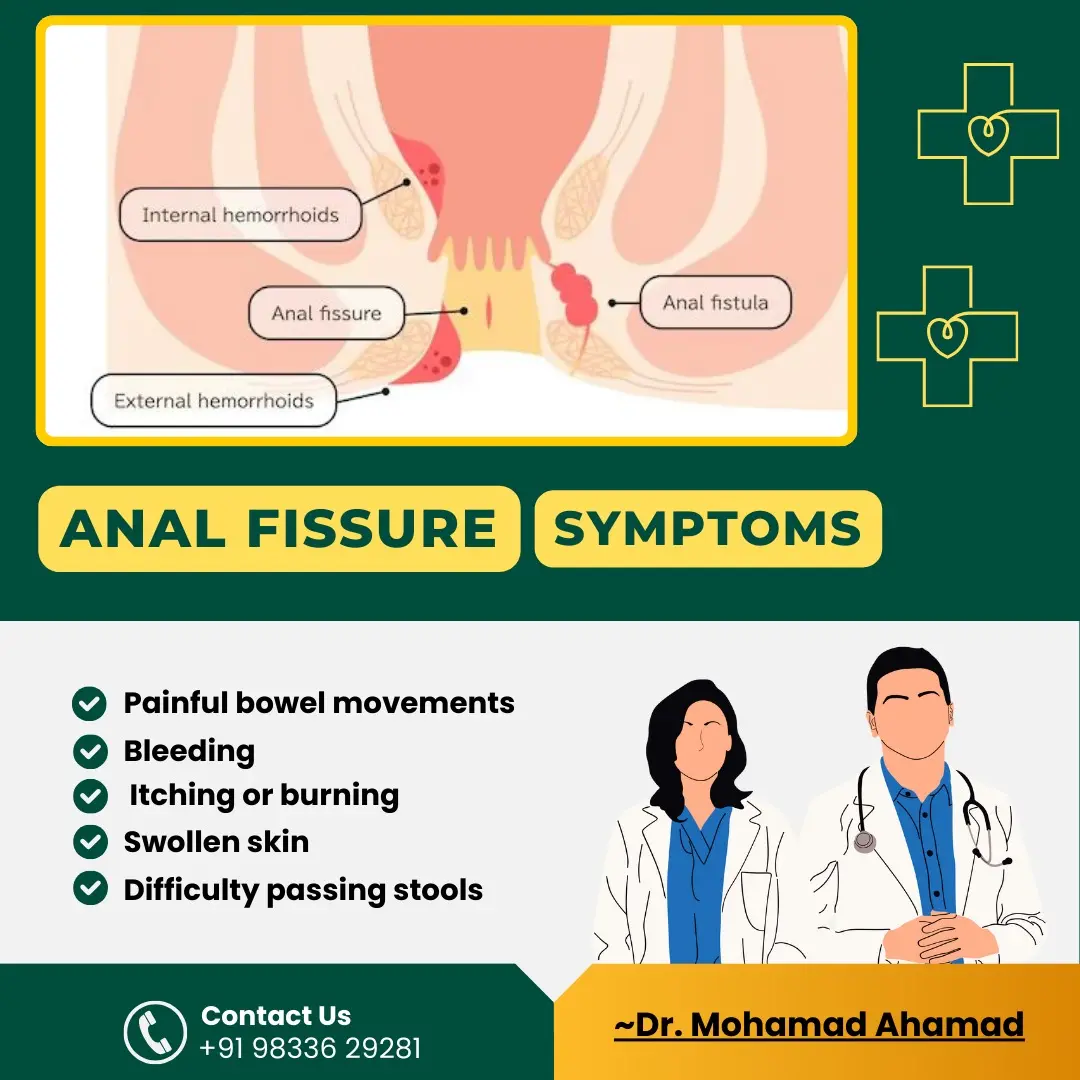
Common Symptoms
Patients with fissure in ano often experience the following symptoms:
- Sharp pain during bowel movements
- Burning sensation after defecation
- Bright red blood on toilet paper or stools
- Itching or irritation around the anus
- Visible crack in the skin around the anus
| Symptom | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | Very common | Moderate to severe |
| Bleeding | Common | Mild to moderate |
| Itching | Less common | Mild |
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing a fissure in ano:
- Age: More common in young to middle-aged adults
- Dietary habits: Low-fiber diets
-
Certain medical conditions:
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Crohn's disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Anal hygiene practices
Understanding these aspects of fissure in ano is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. With this knowledge, we can now explore the various diagnostic methods and medical assessments used to confirm the condition and determine its severity.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
When it comes to diagnosing a fissure in ano, a thorough medical assessment is crucial. This process typically involves several steps to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
A. Physical Examination
The cornerstone of diagnosis is a careful physical examination. This usually includes:
- Visual inspection of the anal area
- Digital rectal examination (DRE)
- Anoscopy for a more detailed view
During the examination, the doctor will look for:
- Visible tear in the anal canal
- Signs of inflammation or infection
- Presence of sentinel pile (skin tag)
- Muscle spasms in the anal sphincter
B. Diagnostic Tests
While a physical exam is often sufficient, additional tests may be necessary in some cases:
| Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Endoanal ultrasound | Evaluates sphincter muscle integrity |
| Anorectal manometry | Measures anal canal pressures |
| MRI | Assesses complex fistulas or abscesses |
| Colonoscopy | Rules out other colorectal conditions |
C. Differential Diagnosis
It's important to distinguish fissure in ano from other conditions with similar symptoms:
- Hemorrhoids
- Anal abscess
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Sexually transmitted infections
- Anal cancer
By considering these possibilities, healthcare providers can ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for patients presenting with anal pain or bleeding.
Conservative Treatment Options
A. Dietary Modifications
Dietary changes play a crucial role in managing fissure in ano. Increasing fiber intake and maintaining proper hydration can significantly improve symptoms and promote healing. Here's a list of recommended dietary modifications:
- Consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber daily
- Drink 8-10 glasses of water per day
- Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet
- Consider fiber supplements if needed
B. Topical Medications
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against fissures. These medications help reduce pain, promote healing, and relax the anal sphincter. Here's a comparison of common topical medications:
| Medication | Purpose | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Nitroglycerin ointment | Increases blood flow, relaxes sphincter | 2-3 times daily |
| Calcium channel blockers | Relaxes sphincter, reduces pain | 2-3 times daily |
| Lidocaine | Provides temporary pain relief | As needed before bowel movements |
C. Sitz Baths
Sitz baths are a simple yet effective treatment for fissure in ano. They involve sitting in warm water for 10-15 minutes, several times a day. Benefits include:
- Improved blood circulation to the anal area
- Relaxation of the anal sphincter
- Reduced pain and discomfort
- Promotion of healing
D. Pain Management Techniques
Managing pain is essential for comfort and to prevent further irritation. Some effective pain management techniques include:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen)
- Application of cold compresses
- Gentle cleaning with fragrance-free wipes or warm water
- Avoiding straining during bowel movements
These conservative treatment options often provide significant relief and can lead to healing in many cases. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, surgical interventions may be necessary.
Surgical Interventions
When conservative treatments fail to heal a fissure in ano, surgical interventions may be necessary. These procedures aim to reduce anal sphincter pressure and promote healing. Let's explore the most common surgical options:
A. Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy
This gold-standard procedure involves making a small incision in the internal anal sphincter muscle to reduce pressure and promote healing. It's highly effective but carries a small risk of incontinence.
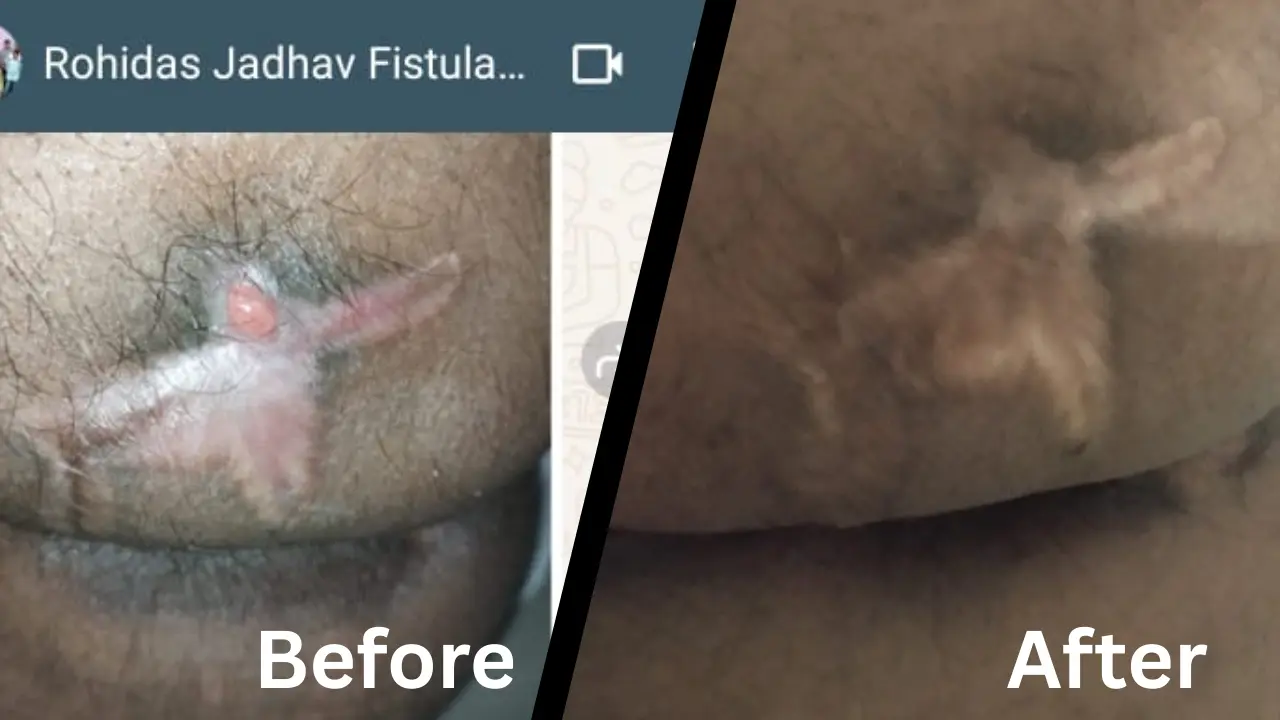
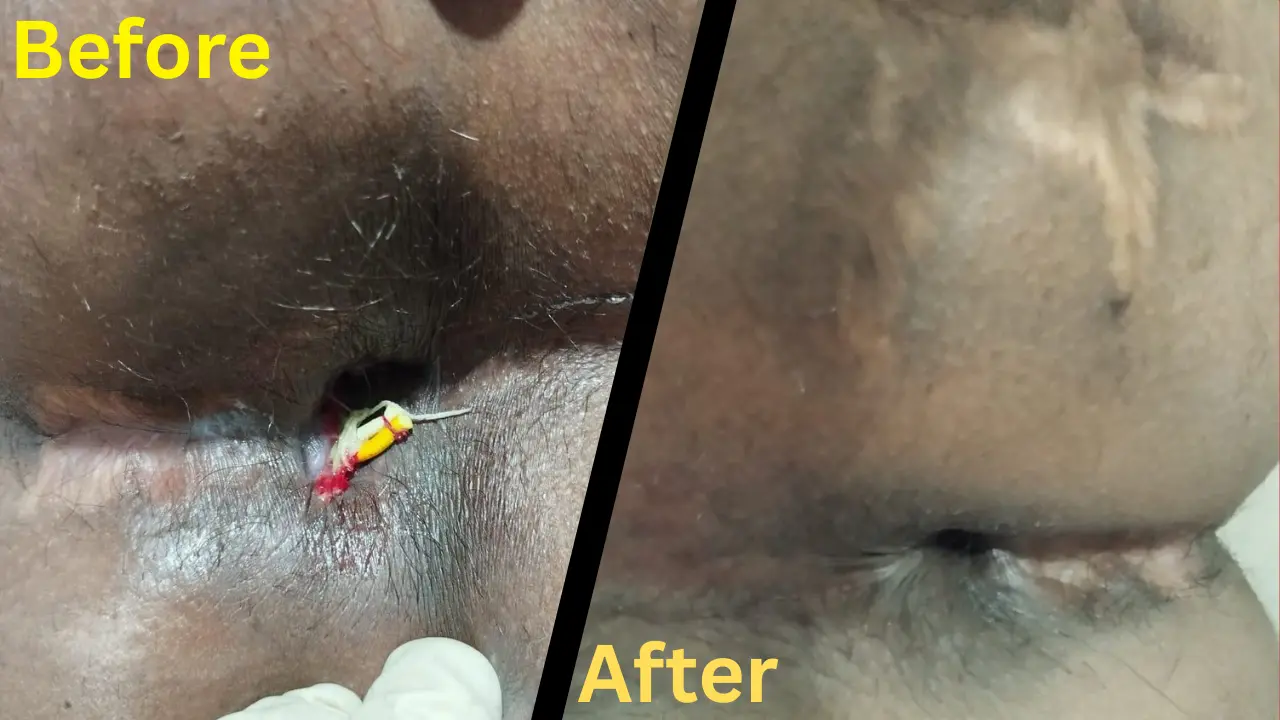
B. Fissurectomy
Fissurectomy involves surgically removing the fissure and surrounding tissue. This procedure is often combined with other techniques for better results.
C. Botox Injections
While not strictly surgical, Botox injections are a minimally invasive option. They temporarily paralyze the anal sphincter, reducing pressure and allowing the fissure to heal.
D. Advancement Flap Procedures
These techniques involve using healthy tissue to cover the fissure, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of recurrence.
Here's a comparison of these surgical interventions:
| Procedure | Success Rate | Recovery Time | Risk of Incontinence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy | 95% | 2-3 weeks | 3-5% |
| Fissurectomy | 85-90% | 4-6 weeks | Low |
| Botox Injections | 60-80% | 1-2 weeks | Very Low |
| Advancement Flap | 85-90% | 3-4 weeks | Low |
Key considerations for choosing a surgical intervention include:
- Severity and chronicity of the fissure
- Patient's overall health
- Previous treatments attempted
- Surgeon's expertise
With these surgical options available, most patients can find relief from chronic fissures. The next section will discuss important lifestyle changes and preventive measures to avoid recurrence after treatment.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing fissure in ano and maintaining overall anal health involves adopting certain lifestyle changes and practicing good habits. Let's explore some effective strategies:
A. Proper hygiene practices
Maintaining proper anal hygiene is crucial in preventing fissures. Here are some key practices:
- Clean the area gently with warm water after bowel movements
- Use soft, unscented toilet paper or wet wipes
- Avoid using harsh soaps or cleansers in the anal area
- Pat the area dry instead of rubbing
B. Dietary fiber intake
Increasing fiber in your diet can significantly reduce the risk of fissures:
| Food Type | High-Fiber Examples |
|---|---|
| Fruits | Apples, pears, berries |
| Vegetables | Broccoli, carrots, spinach |
| Grains | Whole wheat bread, oatmeal |
| Legumes | Lentils, beans, chickpeas |
Aim for 25-30 grams of fiber daily to promote soft, easy-to-pass stools.
C. Hydration importance
Staying well-hydrated is essential for preventing constipation and maintaining soft stools. Drink at least 8 glasses of water daily and increase intake during physical activity or hot weather.
D. Regular exercise benefits
Exercise promotes healthy bowel function and reduces constipation risk. Incorporate these activities into your routine:
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Yoga
- Cycling
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
E. Stress reduction techniques
Chronic stress can contribute to digestive issues and increase the risk of fissures. Try these stress-reduction methods:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Meditation
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Regular sleep schedule
By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing fissure in ano and promote overall anal health. Next, we'll discuss recovery and follow-up care for those who have experienced this condition.
Recovery and Follow-up Care
Post-treatment expectations
After treatment for fissure in ano, patients can expect gradual healing over several weeks. Pain typically subsides within days, but complete recovery may take 4-6 weeks. Bowel movements should become less painful, and bleeding should decrease or stop entirely.
Wound care guidelines
Proper wound care is crucial for optimal healing:
- Keep the area clean and dry
- Use mild, fragrance-free soap when washing
- Pat dry gently after bathing
- Apply prescribed ointments as directed
- Wear loose, breathable clothing
| Do's | Don'ts |
|---|---|
| Use sitz baths | Use harsh soaps |
| Follow a high-fiber diet | Strain during bowel movements |
| Stay hydrated | Ignore signs of infection |
Potential complications
While rare, complications may occur:
- Infection
- Recurrence of fissure
- Incontinence (temporary or permanent)
- Delayed healing
Long-term management strategies
To prevent recurrence and maintain anal health:
- Maintain a high-fiber diet
- Stay well-hydrated
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid prolonged toilet sitting
- Use stool softeners if needed
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing progress and address any concerns. Patients should report any persistent pain, bleeding, or other unusual symptoms promptly. With proper care and lifestyle adjustments, most patients can expect a full recovery and reduced risk of future fissures.
Fissure in ano can be a challenging and uncomfortable condition, but with proper understanding and management, patients can find relief and improved quality of life. From conservative treatments like dietary changes and topical medications to surgical interventions in severe cases, there are various options available to address this issue. The key lies in early diagnosis, appropriate treatment selection, and consistent follow-up care.
Remember, prevention plays a crucial role in managing fissure in ano. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, maintaining proper hygiene, and staying vigilant about your digestive health, you can reduce the risk of developing or exacerbating this condition. If you're experiencing symptoms, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. With the right approach, you can overcome fissure in ano and regain comfort in your daily life.